Definition Although the overall percentage of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere may seem small, greenhouse gases have the unique ability to absorb thermal energy, unlike nongreenhouses gases like oxygen and nitrogen Greenhouse gases act as a layer of insulation around the planet, keeping Earth's surface at a habitable temperature and The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone, Greenhouse gases are gases in Earth's atmosphere that trap heat They let sunlight pass through the atmosphere, but they prevent the heat that the sunlight brings from leaving the atmosphere The main greenhouse gases are Water vapor Carbon dioxide Methane

Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science
Greenhouses gases definition kids
Greenhouses gases definition kids-Definition Greenhouse gases are those gaseous constituents of the atmosphere, both natural and anthropogenic, that absorb and emit radiation at specific wavelengths within the spectrum of infrared radiation emitted by the Earth's surface, the atmosphere and clouds This property causes the greenhouse effectThe greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of life Human action, however, has increased the presence of



Greenhouse Gas Definitions Meanings That Nobody Will Tell You
Greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases (To a lesser extent, surfacelevel ozone, nitrous oxides, andScientists attribute the global warming trend observed since the mid th century to the human expansion of the "greenhouse effect" 1 — warming that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere block heat from escaping Longlived gases that remain semipermanently in the atmosphere and do not respondGreenhouse effect, a warming of Earth 's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect
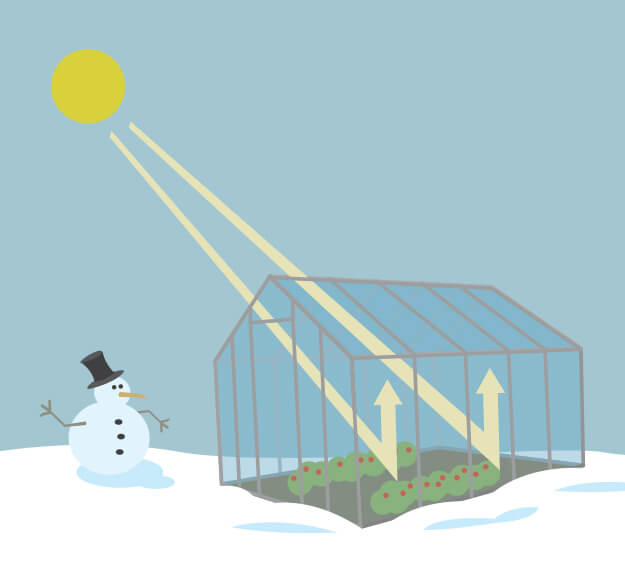
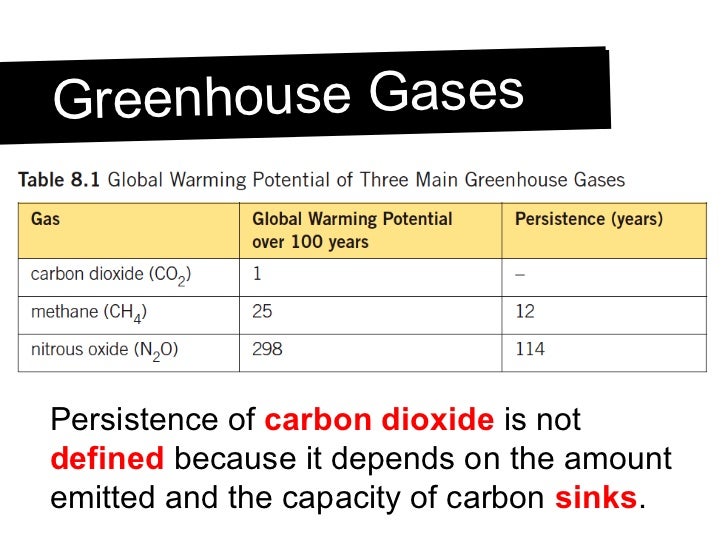
Greenhouse Gases CHAPTER 4 Why some gases are greenhouse gases, but most aren't, and some are stronger than others About Gases The layer model is what is called an idealization of the real world It has the essential ingredient of the greenhouse effect, but it is missing numerous things that are important in the real atmosphere The usual way of comparing greenhouse gases is through a single conversion factor, called the global warming potential, which uses a somewhat arbitrarily chosen time horizon of 100 years For methane, this is usually given as a factor of 25 (that is, methane is 25 times more potent than carbon dioxide)In short it is the natural process that warms the Earth's surface The process is called the greenhouse effect because the exchange of incoming and outgoing radiation that warms the planet works in a similar way to a greenhouse
Define greenhouse gas greenhouse gas synonyms, greenhouse gas pronunciation, greenhouse gas translation, English dictionary definition of greenhouse gas n Any of the atmospheric gases that contribute to the greenhouse effectDefinition of greenhouse gas any of various gaseous compounds (such as carbon dioxide or methane) that absorb infrared radiation, trap heat in the atmosphere, and contribute to the greenhouse effect Water vapor is an important gas for the study of climate and weather because of its role as a natural greenhouse gas as well as its relationship to clouds and precipitationWhat are greenhouse gases?




Ppt Environmental Chemistry Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Greenhouse Gases Biology Notes For Igcse 14
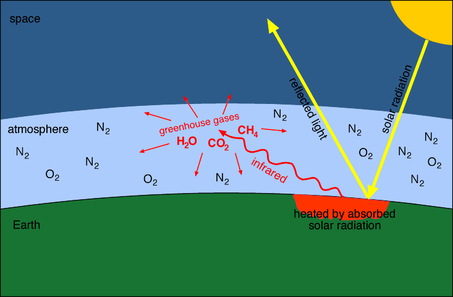
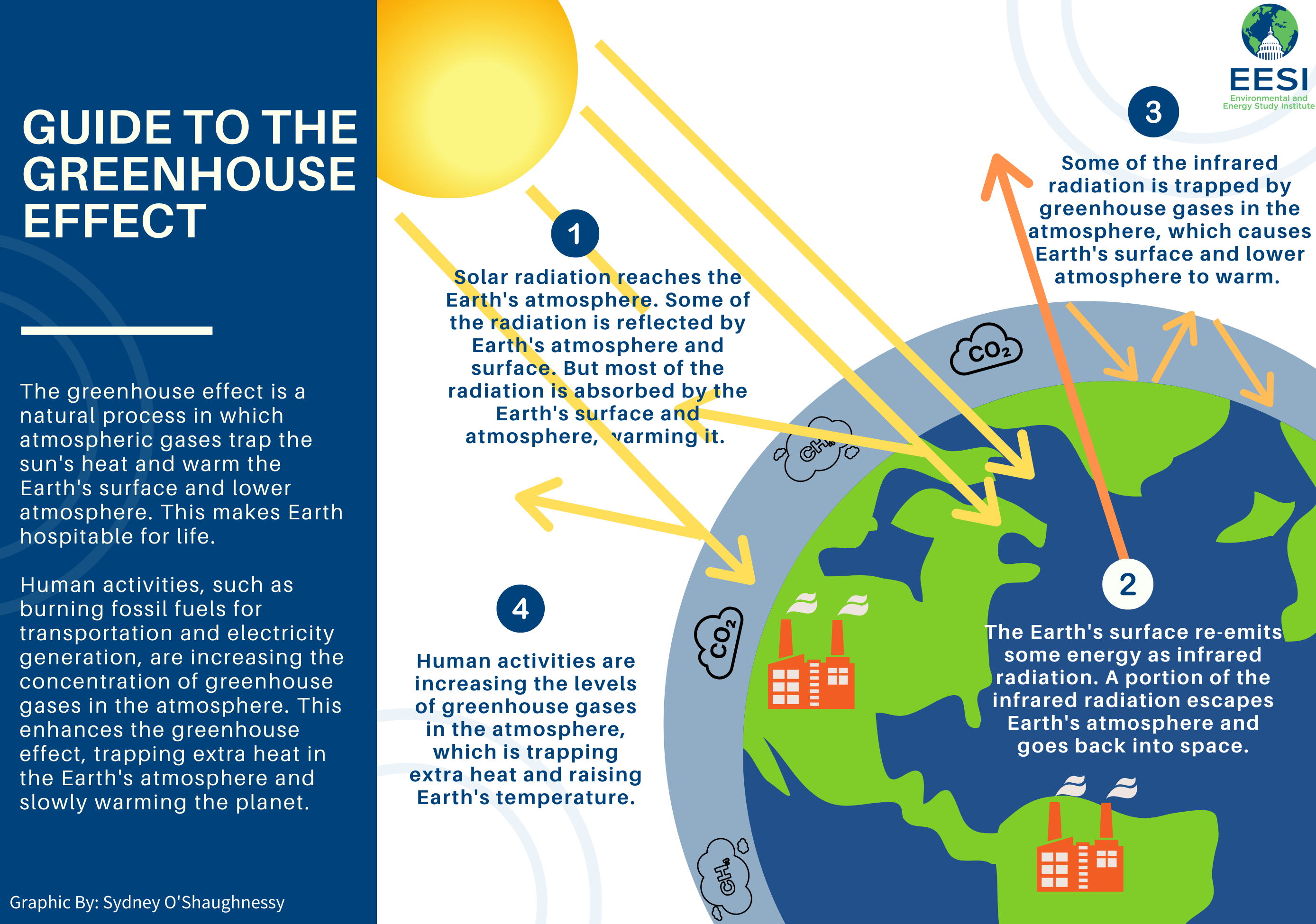
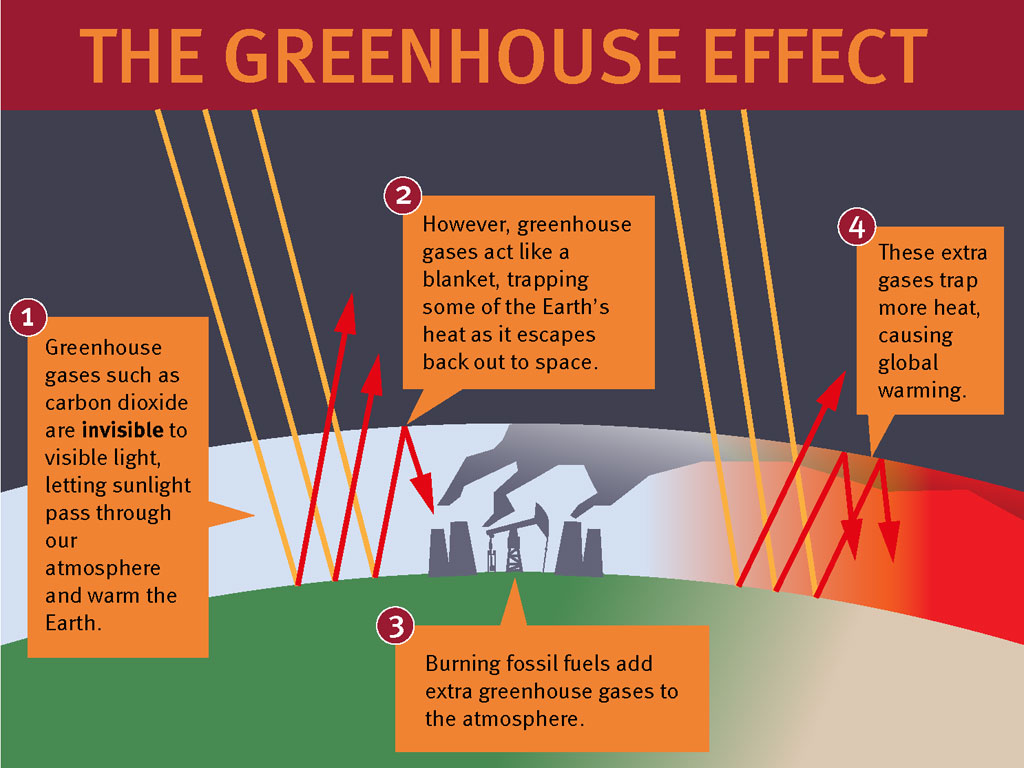
Amplifying the greenhouse effect Like other gases in the atmosphere, including oxygen and nitrogen, greenhouse gases are largely transparent to incoming sunlight But unlike those gases, greenhouse gases are not transparent to outgoing heat (longwave infrared radiation), which radiates from the sunwarmed surface of Earth day and nightThey include methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, and halogenated gases Some of these gases make significant contributions to changing the radiation balance of our planet Other important information for understanding the role of greenhouse gases in climate science characteristics of a greenhouse gas greenhouse gasesManmade greenhouse gas emissions can be divided into those that arise from the combustion of fuels to produce energy, and those generated by other processes Around two thirds of greenhouse gas emissions arise from the combustion of fuels Energy may be produced at the point of consumption, or by a generator for consumption by others




Weatherquestions Com What Is The Greenhouse Effect What Are Greenhouse Gases




Global Warming Definition And Meaning Market Business News
Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions and Removals slide 1 of 4 GHGs are gases that trap heat in the atmosphere Learn more about GHGs » Explore GHG emissions from the largest sources and sectors through Data Highlights » and map app, FLIGHT » Translate abstract GHG measurements into concrete terms that are easy to understandGreenhouse gas meaning 1 a gas that causes the greenhouse effect, especially carbon dioxide 2 a gas that causes the Learn moreGreenhouse gas definition 1 a gas that causes the greenhouse effect, especially carbon dioxide 2 a gas that causes the Learn more



Economic Approaches To Greenhouse Warming



Global Warming Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Faq Eesi
A greenhouse gas is a gas which reflects radiation that the Earth emits, and stops it from being lost into space This makes the Earth hotter than it would be without greenhouse gases This is called the " greenhouse effect " The greenhouse effect keeps the temperatures on our planet mild and suitable for living things Greenhouse gases (GHG) include carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, ozone, nitrous oxide and fluorinated gases These molecules in our atmosphere are called greenhouse gases because they absorb heat The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides




What Is The Greenhouse Effect The Environment For Kids Updated Version Youtube




Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate U S Energy Information Administration Eia
Definition Greenhouse gas emissions refer to carbon dioxide and other chemical compounds that contribute to global climate change Vital Signs tracks greenhouse gas emissions linked to consumption from the three largest sources in the region surface transportation, electricity consumption, and natural gas consumptionMany chemical compounds in the atmosphere act as greenhouse gases These gases allow sunlight (shortwave radiation) to freely pass through the Earth's atmosphere and heat the land and oceans The warmed Earth releases this heat in the form of infrared light (longwave radiation), invisible to human eyes1 Some of theGreenhouse gas definition, any of the gases whose absorption of solar radiation is responsible for the greenhouse effect, including carbon dioxide,



Global Warming Images




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey
Define greenhouse gases greenhouse gases synonyms, greenhouse gases pronunciation, greenhouse gases translation, English dictionary definition of greenhouse gases Carbon dioxide, methane, chlorofluorocarbons, nitrous oxide and lowlevel ozoneWortformen (plural) greenhouse gases Substantiv ( Extractive engineering General) A greenhouse gas is a gas that contributes to the greenhouse effect by absorbing infrared radiation in the atmosphere Carbon dioxide is considered to be a greenhouse gas because it traps heat radiated into the atmosphere Carbon dioxide is widely consideredIn terms of the net increase in the greenhouse effect due to humanproduced greenhouse gases, CO 2 is responsible for the lion's share CO 2 from fossil fuel burning alone is more than half the net force If you add CO 2 from fossil fuel burning, deforestation, and other minor sources, this comes to a little more than threefourths of the net




What Is Greenhouse Gases Sources Effects And List




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
Greenhouse effect definition is warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of a planet (such as Earth or Venus) that is caused by conversion of solar radiation into heat in a process involving selective transmission of short wave solar radiation by the atmosphere, its absorption by the planet's surface, and reradiation as infrared which is absorbed and partlyThese "greenhouse gases" allow the sun's rays to pass through and warm the planet but prevent this warmth from escaping the atmosphere into space Without them, Earth would be too cold to sustain life as we know it When we talk about greenhouse gases, we're referring to carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons and sulphur The greenhouse effect, in turn, is one of the leading causes of global warming The most significant greenhouse gases, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), are water vapor (H2O




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society
Greenhouse gases absorb this infrared radiation and trap its heat in the atmosphere, creating a greenhouse effect that results in global warming and climate change Many gases exhibit these greenhouse properties Some gases occur naturally and are also produced by human activities Some, such as industrial gases, are exclusively human made Percentages may not add up to 100% due to independent rounding Larger image to save or print Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere are called greenhouse gases This section provides information on emissions and removals of the The term "greenhouse effect" is mentioned a lot when we talk about climate change But what exactly does it mean?




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Global Warming Potential Definition And Examples
Greenhouse gases have very different warming effects one tonne of methane does not have the same impact on warming as one tonne of CO 2Carbon dioxide equivalents (CO 2 e) attempt to convert the warming impact of the range of greenhouse gases into a single metric This is done by multiplying each gas by its 100year 'global warming potential' value the amount of warming oneGreenhouse Gas Emissions Methodology and Documentation Greenhouse Gas Emissions Crossroads Hollywood Methodology and Documentation August 16 Page 4 Table 1 Description of Identified Greenhouse Gasesa Greenhouse Gas General Description Carbon Dioxide (CO2) An odorless, colorless GHG, which has both natural and anthropocentric sources Greenhouse gas emissions definition the emission into the earth's atmosphere of any of various gases , esp carbon dioxide , Meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples




Greenhouse Gas Is Greenhouse Gas Emissions Environment 21



Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gas es—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gases sometimes known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)Main Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs lived




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Greenhouse Gases And The Greenhouse Effect Kids Environment Kids Health National Institute Of Environmental Health Sciences




Greenhouse Effect Definition Gamesmartz




Greenhouse Gases Highwire Earth



What Are Greenhouse Gases A Detailed Overview Common Issues




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect E 3 Pages Definitions 2 Description 3 Greenhouse Gases 4 Greenhouse Gases Effect On Atmosphere Ppt Download




Click On The Image To View The High Definition Version Create Infographics At Http Venngage Com How To Create Infographics Food Insecurity Greenhouse Gases




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




Methane Climate Clean Air Coalition




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




Methodological Framework To Define The Cost And Effectiveness Of Download Scientific Diagram



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia



Archive Codes Of Good Agricultural Practice Definitions Greenhouse Gases Definition




Greenhouse Effect Definition Suns Rays Are Trapped By




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




The Greenhouse Effect Presenters Jaime Pinto Nathalie Mokuba Ppt Video Online Download




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Greenhouse Gases



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




Scope Definition By Ghg Protocol 22 Download Scientific Diagram




Cost 356 Towards The Definition Of A Measurable




What Is Greenhouse Gas Definition Causes Effects Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Space




Carbon Dioxide Controls Earth S Temperature




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Untitled Document




Which Gases Are Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society




Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change




Solved Match The Terms With The Proper Definition A N Chegg Com




Green House Effect Definition Meaning Video For Kids Youtube




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




Climate Change Natural And Anthropogenic Causes Yo Nature Climate Change Climates Greenhouse Gases




The Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gasses




Greenhouse Gas Ghg Meaning And Several Examples




Topic 7 Wrap Up The Radiation Laws And



Greenhouse Gas Definitions Meanings That Nobody Will Tell You



Hamburg Open Online University



1



What Does Carbon Footprint Mean Definition Of Carbon Footprint Carbon Footprint Stands For An Estimate Of The Amount Of Greenhouse Gases Created By The Use Of Fossil Fuels In A




Environmental Chemistry Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ppt Download




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Carbon Dioxide Greenhouse Gas Definition Png Clipart Brand Carbon Cycle Carbon Dioxide



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate



Greenhouse Gases
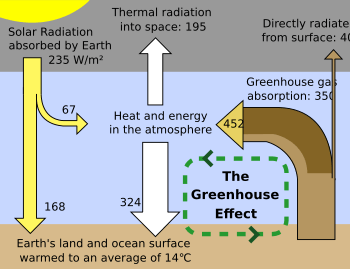



Greenhouse Gas Facts For Kids



What Does Greenhouse Gases Mean Definition Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gases Stands For Carbon Dioxide And Other Gaseous Emissions Resulting From Human Activity That Cause Heat To Be Trapped In




Pdf Cosmic Theories And Greenhouse Gases As Explanations Of Global Warming Semantic Scholar




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Definition Impact Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Lesson For Kids Study Com




Extended Definition The Greenhouse Effect Cleanairdawson




Greenhouses And The Green House Effects Done By




Cap And Trade What Does It Mean For




Climate Class A Greenhouse Gas Primer Best



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids



1




Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Methane Definition Properties Uses Facts Britannica




Full Size Picture A5greenhouse In 21 Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gases Effect
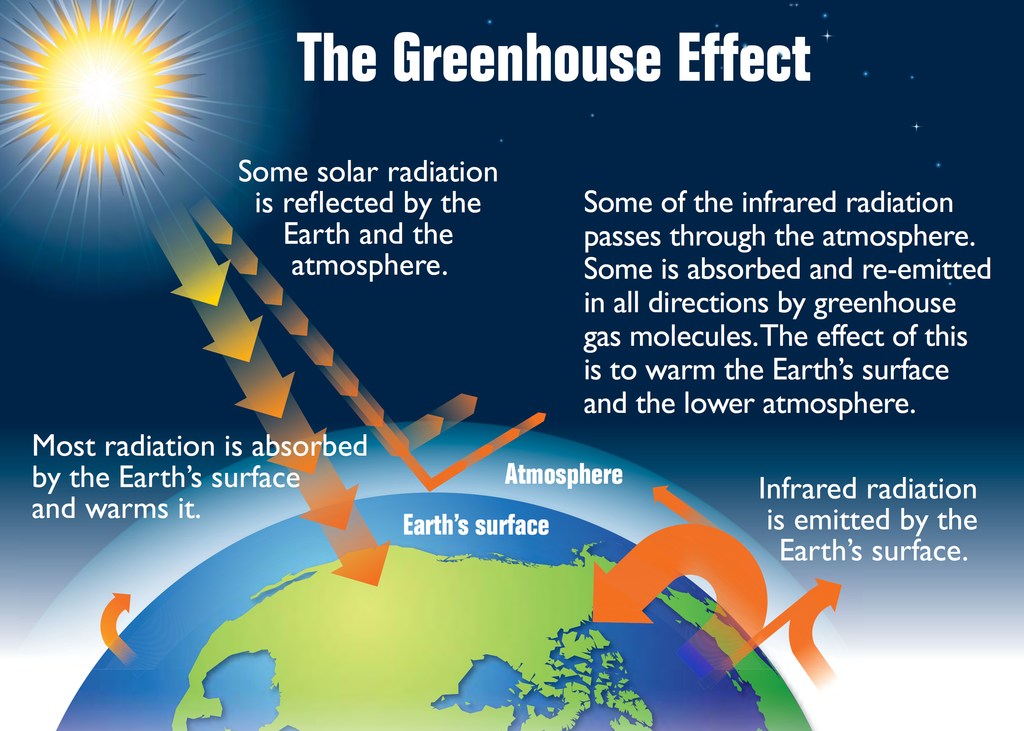



What Is The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
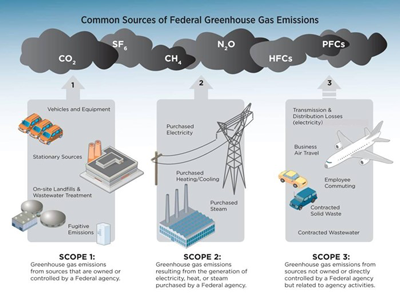



Greenhouse Gases At Epa Us Epa




Implications Of Possible Interpretations Of Greenhouse Gas Balance In The Paris Agreement Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society A Mathematical Physical And Engineering Sciences




Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Greenhouse Effect What Is It Definition And Role In Global Warming




Greenhouse Gases Global Warming Definition Essay




Explainer Co2 And Other Greenhouse Gases Science News For Students




Section 3 Remote Sensing Of Global Change Greenhouse
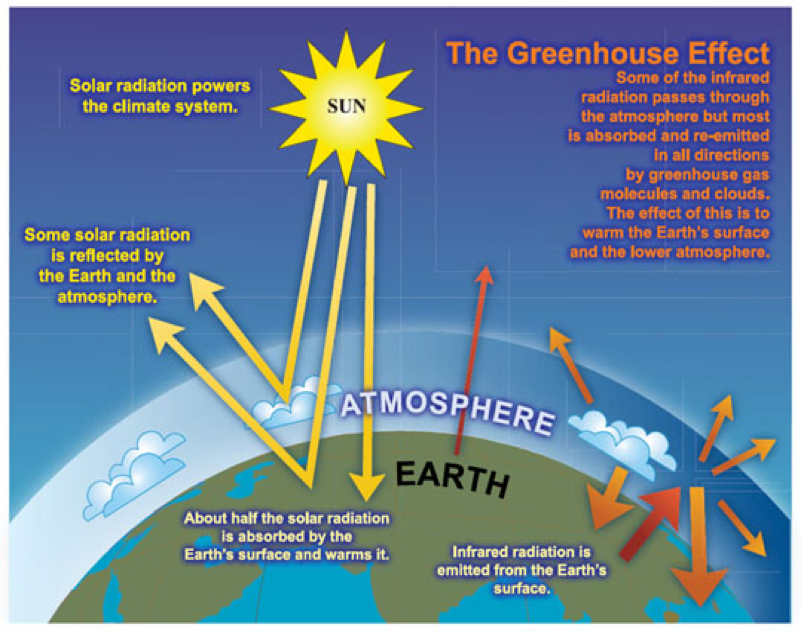



Greenhouse Gas Reduction
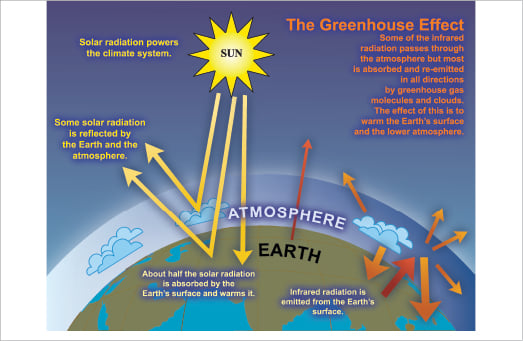



Faq 1 3 Ar4 Wgi Chapter 1 Historical Overview Of Climate Change Science
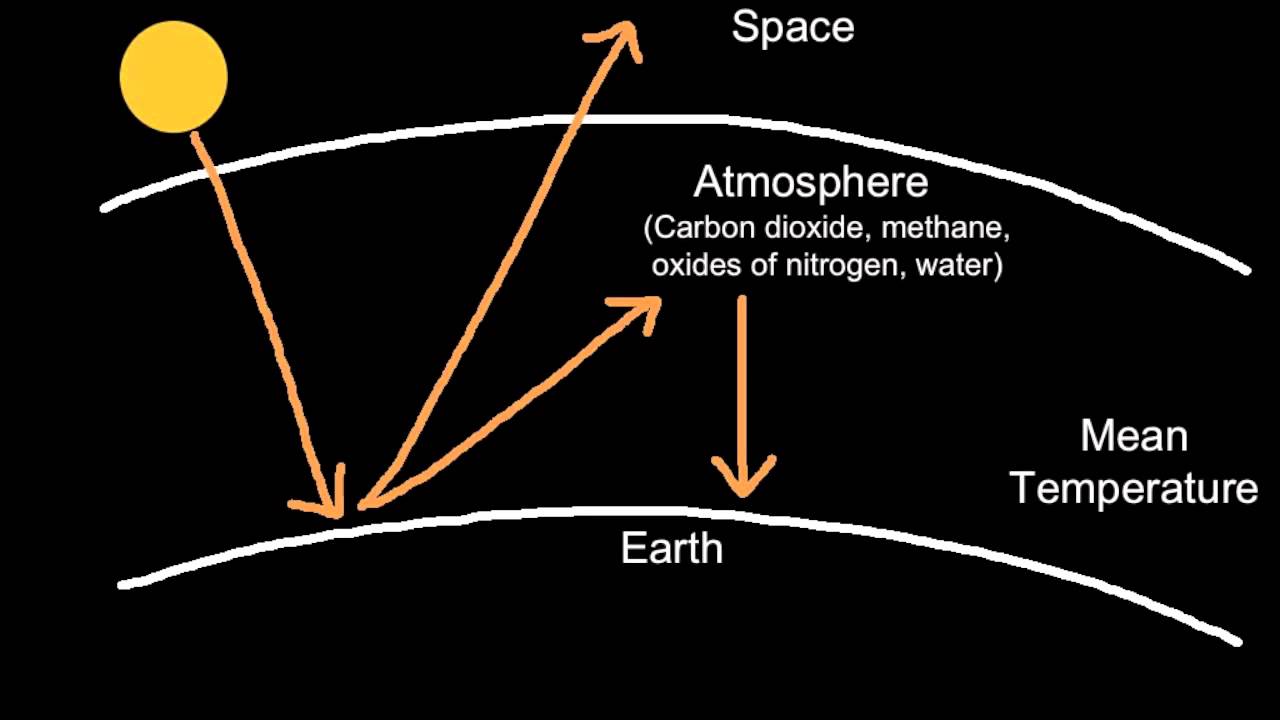



5 2 3 Explain The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Youtube




Learnsustainability Greenhouse Gases



Environment For Kids Global Warming



3




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Climate Change Climate Change Background The Earth Has Been In A Warming Trend For The Past Few Centuries Mainly Due To The Increase In Greenhouse Ppt Download




Define Green House Gases With Its Effects Qs Study



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿